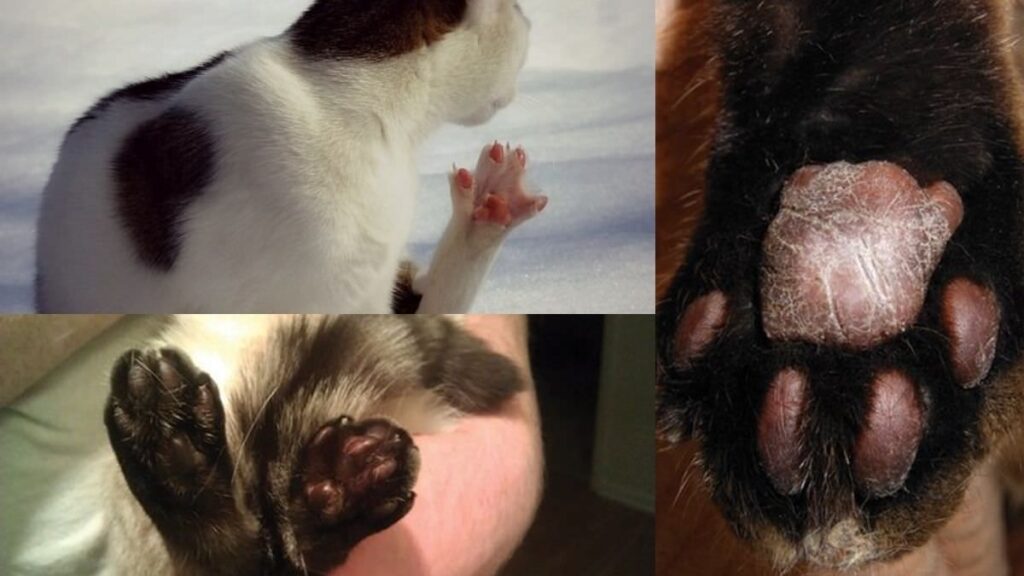
Wondering about Pillow foot in humans? Let’s see all about pillow foot and whether it affects humans or not in this article.
What is pillow foot?
Pillow foot, medically termed as pododermatitis, is an inflammation of the skin of the paw of cats and dogs. It may manifest in the tissues of the footpads, nail folds, interdigital spaces, and nails. It can affect both felines and canines in a close proximation of one or more feet. The condition is characterized by sudden flare-ups, that may sometimes subside on its own. However, in some cases, it might become chronic, requiring lifelong medical treatment.
Symptoms of Pillow Foot
Symptoms include the spongy texture of the affected paw, one or more lesions on the affected paw, which may be accompanied by redness, itchiness, pruritis, swelling, ulcers, hair loss, pain, and lameness. The cat or dog may lick the affected paw or paws often and may chew and bite, causing bleeding sores. If untreated, it can sometimes lead to lethargy, loss of appetite, and also renal complications.
Pillow Foot in Humans
As stated earlier, pillow foot only affects animals like cats and dogs and it doesn’t impact humans. Therefore, the disease can not be transmitted to humans by either cats or even dogs. But even if it doesn’t affect humans, it can cause severe problems to your pet and thereby cause discomfort.
Causes of Pillow Foot
Causes for pillow foot can vary; it can be merely a skin problem or can point to an underlying disease. The cause of pillow foot can be more than one. Common causes include:
- Parasitic Infection
- Foreign bodies like grass seeds can get into the skin of the paw when the animal is walking or running on grass
- Allergies caused by food or environmental allergens like dust mites or pollen,
- Fungal or bacterial infections, s
- Stress
- Obesity causes excessive pressure on the feet, which can lead to blisters on the paw
- Certain hormonal diseases
- In some cases, it can also be due to autoimmune disorders.
Diagnosis
A thorough physical examination by a vet and the clinical symptoms are enough to confirm the diagnosis of pillow foot. But, he may ask for additional tests to find out the reason for the condition.
To test for a mite infestation, the vet may take samples of your pet’s hair and skin scraping for further testing. If the fluid discharge is present in the lesions, it may be collected, analyzed, or cultured to find if an infectious organism is present.
X-rays and surgery are required in case of a foreign body infection. Allergy testing and blood testing to rule out hormonal problems may also be advised.
Treatment Options
Treatment methods and medication are all dependants on the causative factor. If the underlying cause is an infection, then your veteran may prescribe certain antibiotics or antifungals to cure the condition. Hormonal problems also require hormone supplements, and allergies will necessitate the identification and removal of the allergen.
Home remedies for prevention and treatment of the condition include proper foot hygiene, a high protein, ant-inflammatory, and hypoallergenic diet, regular washing and drying of your pet’s paws. Soak the paws in medicated water and use hypoallergenic cleaning products for the floor and your pet’s living areas. It is important always to keep your pet’s litter clean and also keep a watch on the surfaces your pet walks on.
However, if symptoms worsen or your pet is in obvious pain or distress, it is prudent to consult your vet immediately.